Having a cold in summer is, in my opinion, really rude. Typically, these illnesses are associated with cold weather (hence the name), but that’s not actually the case. This is why we can get colds in summer and it is also why the relationship between ACs and colds is little more complicated than we’re led to believe.
This may actually be good news for you. Cold or no cold, in some states, the thought of turning off the AC in summer is enough to make you cry. You still need to be careful, so let’s get into the details to help you navigate hot weather and cold viruses.

Air conditioning can worsen the symptoms of a cold because the air is dried out by these units. Cold, dry air leads to dry mucous membranes, respiratory irritation, and depressed immune systems. The negative effects of air conditioning on colds can depend on how low the temperature is set.
***The use of air conditioning when you have a cold is generally not recommended. Air cooled by air conditioning can create the right type of environment in your home that is perfect for viruses and bacteria to foster and grow
ACs Are Believed to Be Harmful When We’re Sick
It is widely believed that air conditioning can cause colds and make you feel worse if you already have one.
This first claim is untrue, which we’ll cover a little later. But first, let’s look at whether or not it’s OK to use the AC when you have a cold—after all, that’s why you’re here.
Colds are viruses, so air conditioning cannot make them worse in the sense that they become more harmful viruses.
However, according to Dr. Greene, a practicing physician and global health advocate, air conditioning can definitely affect the expression and severity of the symptoms.
How ACs Can Make a Cold Worse
Symptoms of the common cold include:
- Stuffy and/or runny nose
- Sneezing
- Scratchy/sore throat
- Coughing
- Low-grade fever
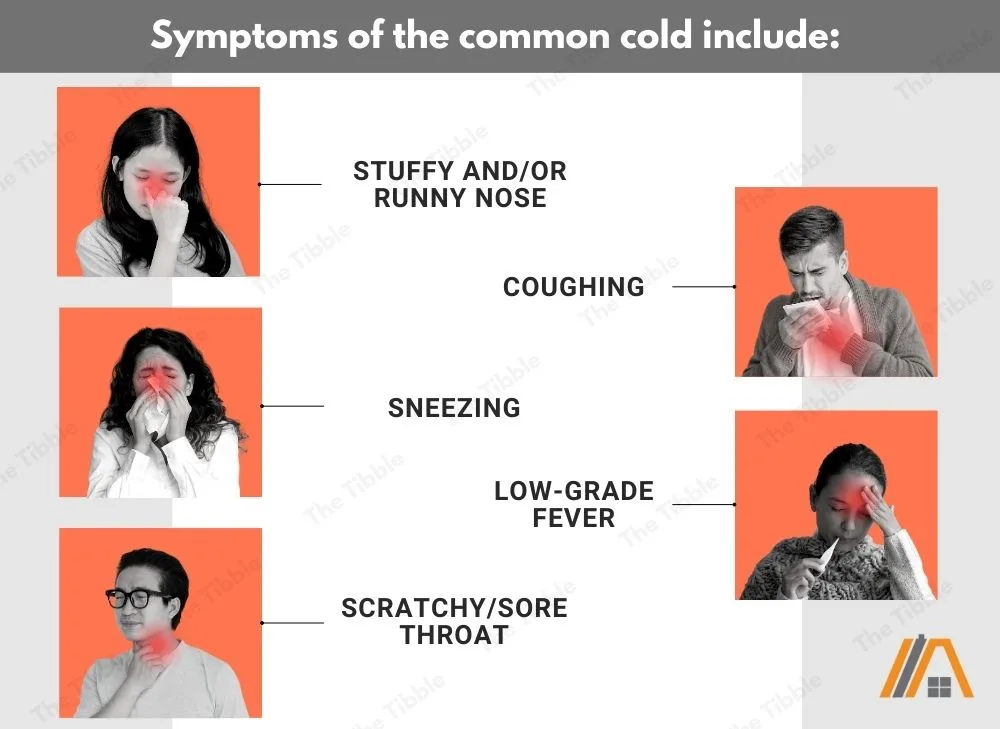
Cold temperatures can negatively affect all of these symptoms.
Air conditioning units remove the moisture from the air when they cool it. This means that the expelled air is drier than it was before. Dry air can dry out mucous membranes and act as an irritant.
Stuffy Noses
Noses get stuffy when the the lining of the nasal passages swell and block the air from coming through. The swelling can result from the irritation caused by dried out membranes.
Runny Noses
In response to the dried out membranes, the body also produces more and more mucous, which results in a runny nose.
While these two responses may seem to cancel each other out, that is not the case in reality. The excess mucous production does not reduce the swelling. The result is a dripping nose that you cannot sniff to stop.
Sneezing
In addition, the irritation of the nasal passages makes you more likely to sneeze, which is a defensive mechanism to “tickles” of our nose and throat, which may indicate the presence of a dangerous substance trying to gain access to our lungs.
Scratchy/Sore Throat
You have mucous membranes lining your throat as well. These are similarly affected by the drier air, particularly if your nose is blocked and you are breathing through your mouth.
This along with the excess mucous running down the back of your throat (post-nasal drip) leads to a raw and scratchy throat. We all know that painful feeling of trying to swallow with a throat in this condition!
Coughing
Coughing, at least, the coughing that you are experiencing as part of your cold is a result of the excess mucous production in your respiratory passages. Without coughing, all of this mucous would get into your lungs and give you pneumonia.
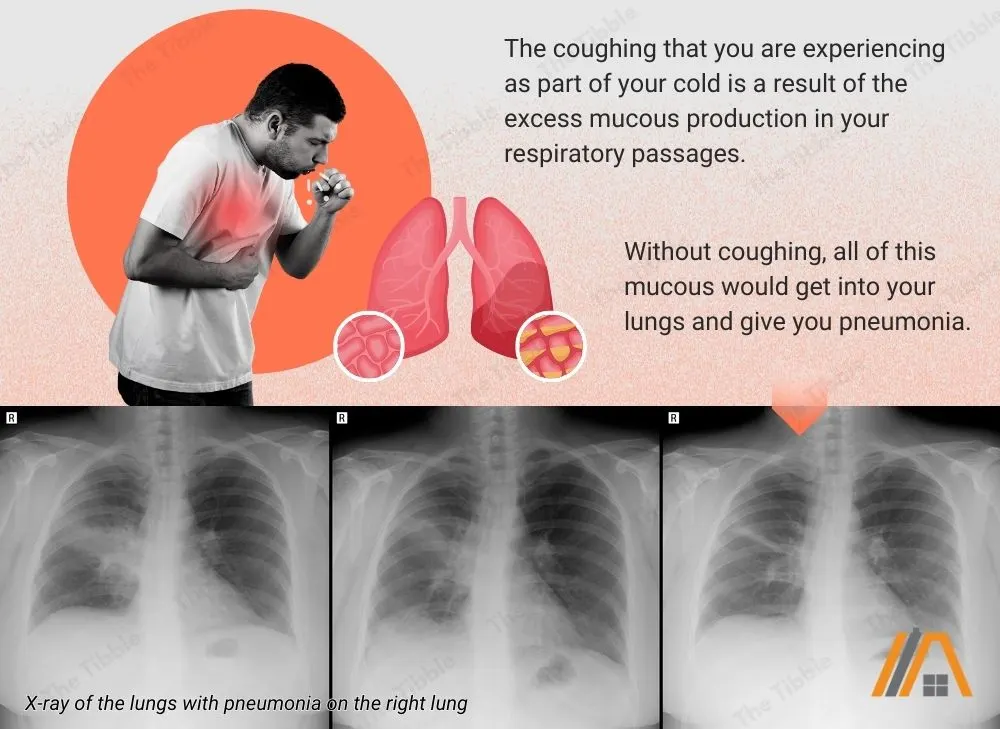
Remember that cold, dry air contributes to the excess production of mucous, so air conditioning can make coughing worse.
In addition, the mucous gets tackier than it should, making it harder to dislodge, which is why the coughing can get quite violent.
Air conditioning can help or worsen allergies, which are often mistaken for colds as these two maladies share similar symptoms. You can read more in: Does Air Conditioning Help With Allergies?
The Effects on Sleep
Running the AC at night seems like a great idea. It cools you down enough to actually get to sleep.
However, your body’s core temperature naturally drops when you are asleep. Cooled air blowing over your cooled body is very disruptive to sleep, even if you are not aware of waking up properly.
Poor sleep is the last thing you need when your body is trying to recover. Sleep is like the ultimate reset for us. It’s as close as we come to “switching it off and then switching it back on” that we can get.
So, disrupted or poor quality sleep as a result of the operating AC unit can prolong our cold symptoms and make us feel generally worse as we add fatigue to everything else.
Temperature of Conditioned Air May Make a Difference
If the outside temperatures are soaring and you bring the inside temperatures down to a moderate number, then you are not exposing your body to the extreme cold and dryness of air at a very low temperature.
However, when it’s so hot outside, it takes a lot of self control not to set the AC as low as it can go.

Personally, I like to need to wear a sweater or hoodie in summer if there is an AC available. This is not a recommendation, though.
Most heating and cooling technicians agree that there should not be a huge difference between the temperature outside and the one in your home or building (unless, of course, it’s one hundred degrees outside).
Even if you don’t have a cold, these low temperatures can be harmful (again, we discuss this further in a later section).
In addition, very cold air conditioning can be the source of mildly uncomfortable ailments like exhaustion, headaches, and sore muscles.
The International Journal of Epidemiology published a study that found evidence that linked air conditioning to constitutional and neurological symptoms like fatigue and headaches.
These symptoms make the effects of your cold seem worse and may even lead you to believe you have influenza as opposed to a cold virus.
Balance It With a Humidifier
If you run a humidifier along with the AC set at a moderate temperature, the air does not dry out as much and your respiratory tract may suffer from less irritation from this source.
Of course, humidifiers add a certain amount of heat back into the air, so you will have to find a good balance between the two.
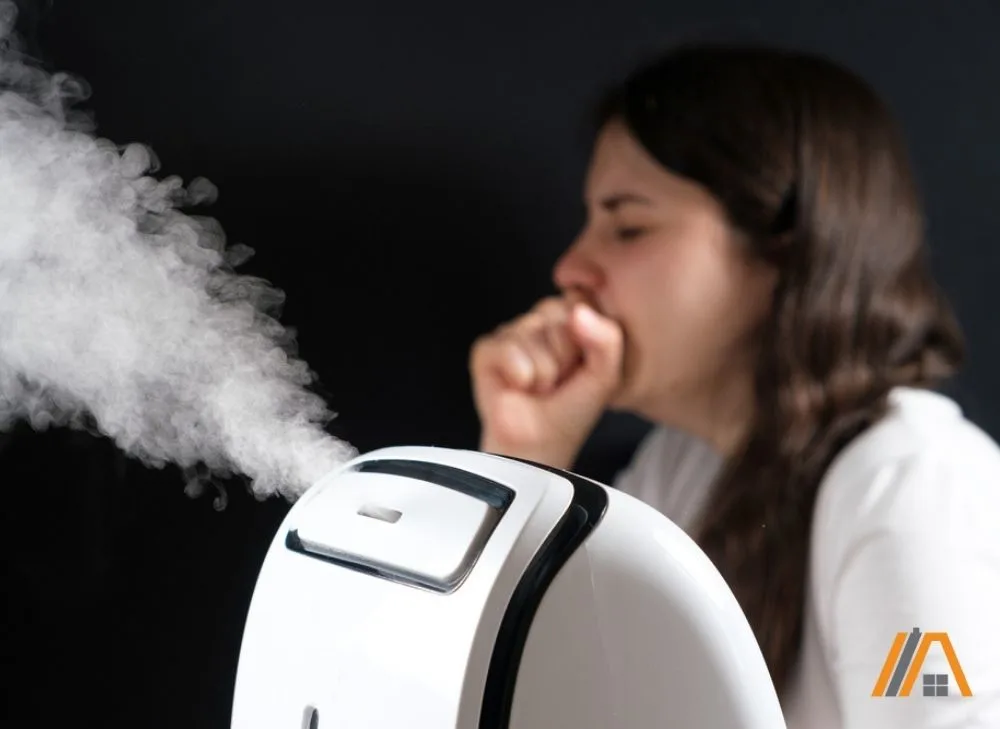

Also, don’t just set your humidifier near your AC. The humidified air will just be sucked straight into the AC and the moisture condensed out.
Cold Doesn’t Cause Colds
While air conditioning can worsen the symptoms of a cold, it cannot actually cause a cold.
If you’ve ever been told that getting caught in the rain, being outside in the cold weather, or sleeping with wet hair will cause you to catch a cold, then you are forgiven for making the assumption that the two are intrinsically linked.
This is solidified by the fact that common colds do often follow after such events.
However, colds are the result of viruses infecting our bodies, typically Rhinoviruses. They are not carried on cold breezes or particularly attracted to people with lower body temperatures.
Johns Hopkins Medicine, a well-known name when it comes to medical research and training, says:
“Contrary to popular belief, cold weather or being chilled doesn’t cause a cold.”
Why Colds Are Associated With Cold Temperatures
While some old wives’ tales seem completely random and nonsensical, claiming that cold weather causes colds is not so out there since there is a correlation even if there is no direct causation.
There are a number of reasons why colds are undeniably connected with getting or being cold.
- Rhinoviruses are known to thrive at lower temperatures, even preferentially replicating in the upper respiratory tract where it is cooler than further down the tract and in the lungs.
- The immune system is suppressed when the body’s temperature is lowered below normal. Bodies need to be kept within a certain temperature range because this is the range at which all the systems work best. Deviation from this compromises function.
- Cold particularly causes the blood vessels near the surface of the body to constrict, taking white blood cells further away and making the body more vulnerable to pathogens.
Going in and out of air-conditioned spaces can particularly depress the immune system by overwhelming the body’s thermoregulatory processes. You can learn more in Can You Get Sick From Going in and out of Air Conditioning
- Cold weather is associated with low humidity in the air. This dries out our mucous membranes. Mucous membranes such as those lining the respiratory tract are supposed to stay moist. This is what traps viruses, bacteria, and the like, preventing them from getting into our systems.
So, in an air conditioned environment, provided the temperatures are low enough and the exposure is long enough, the fact that mucous membranes dry out and immune responses are depressed can leave you vulnerable to any cold viruses in the air.
Air Conditioning Sickness
Even though air conditioning does not directly cause colds or other illnesses, there is a non-medical term for that stuffy, achy feeling often accompanied by a dry cough that seems to come from sitting in a cold house for too long.
The term is air conditioning sickness.
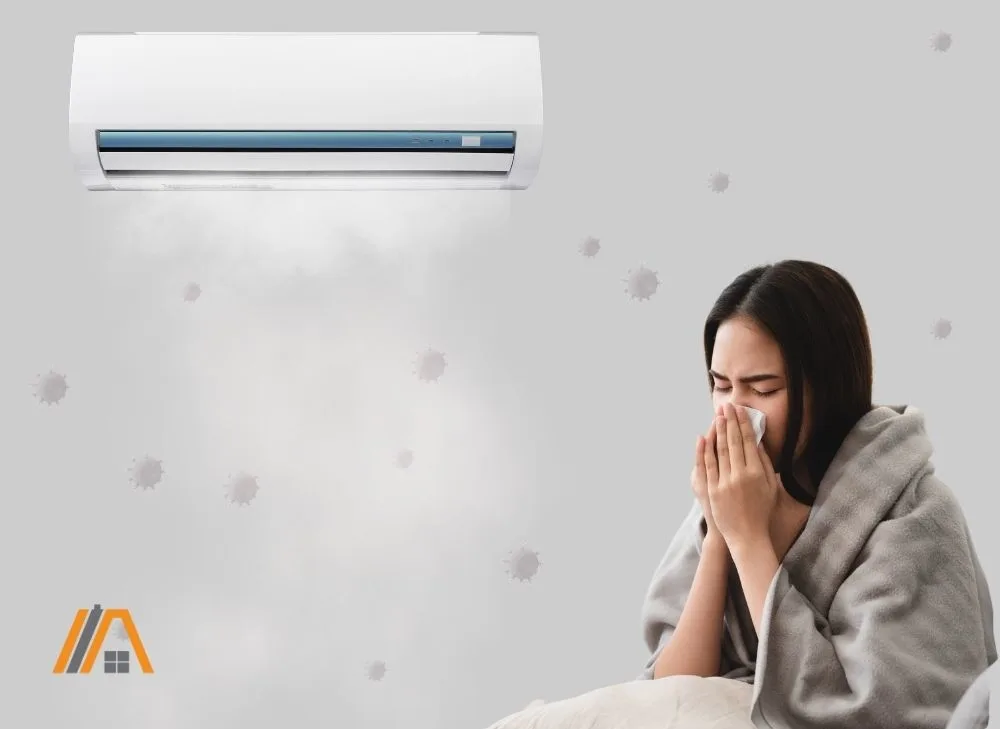

This “condition” is usually caused by bacteria, mold, fungi, dander, and other respiratory ailments that are living or growing in the air-conditioned space.
The movement of air created by the AC unit stirs these particulates up and, once airborne, they can readily be inhaled.
All of these pathogens can actually collect or grow in your AC unit and be circulated into the room with the cooled air.
Because condensation is a by-product of a working air conditioner, it can create a moisture-filled environment that allows bacteria, fungi, and more to thrive.
This coupled with dried-out mucous membranes and a depressed immune system makes falling ill a lot more likely.
Sometimes, there are also ozone-releasing appliances that are responsible for your symptoms, so rule these out too.
