If only Thomas Edison could see us now, what with all the various types of bulbs out in the world today. There are so many, we even have different kinds of sockets. And, when it comes to mixing and matching different bulbs and different sockets, you need to pay attention.
It is possible to use a heat bulb in a regular socket. However, there are determining factors, and certain problems may arise if such factors are not adhered to correctly.

A heat bulb can be used in a regular lamp if the bulb’s wattage does not exceed that of the socket. If it did, the circuit would be overwhelmed, causing damage to the wiring, socket, light fixture, and bulb. If the wattages match, the heat bulb will provide light but no significant heat.
Will Heat Bulb Fit in Regular Socket?
There are multiple types of bases and sockets that a light bulb can have. These various bases and sockets extend to heat bulbs as well as regular bulbs.
Fortunately, at the end of the day, the type of base and socket are not determining factors of whether a heat bulb can be used or fitted within a regular bulb socket.
The range of designs should be similar enough that you would just need to make sure that the regular socket and the heat bulb base match. But this is so logical, it cannot be considered to be the main determining factor.
The real determining factor is taking into consideration the wattage and voltage of the socket and bulb of choice.
Light bulbs pull a certain amount of electric current and lamps or sockets are designed to handle certain ranges of current.
If your regular bulb has a lower wattage than the socket, then the light and heat output will be lower than what the socket can handle and you shouldn’t encounter problems.
Installing a light bulb with a higher wattage than the socket is designed for, results in too much current being pulled. The socket overheats and gets damaged, and the lightbulb can explode.
Most Heat Bulbs Have Higher Wattage than Regular Bulbs
The main difference between heat and regular bulbs is their wattage. Since we have just been talking about how this is the main factor to consider, this is why it’s important to think carefully before mixing their sockets.
Heat bulbs are incandescent light bulbs, meaning the wire filament inside heats until it glows. They reach very high temperatures to produce light and infrared radiation.
Heat bulbs have a higher wattage, and therefore, pull a lot more power than regular bulbs. Unlike regular bulbs, the main function of a heat lamp is not to provide light but to provide warmth and heat, which is useful in the food industry and animal enclosures.
This typically higher wattage is what generally precludes the use of heat bulbs in regular lamps. As mentioned before, if a bulb pulls more power than the socket is designed to handle, the lamp is damaged and the bulb blows, but we will cover this in more detail shortly.
What Is the Fixture’s Wattage Rating?
If you are planning on replacing or interchanging light bulbs, the rating is your guide as to what kind of bulb you can fit without causing serious damage.
Wattage ratings are usually printed on the bulb sockets and the glass or metal base of the bulb.
If you have more than one socket, look out for a label stating the total combined wattage, which means you need to ensure that the total number of bulbs being used does not exceed the total wattage of the lamp.
The wattage rating of a regular bulb can range between 40 and 100 watts, whereas a heat bulb can have a wattage rating of up to 250 watts or more.
Using regular bulbs in heat lamps, including bathroom heat lamps, is less of a hazard, but the regular bulb will obviously yield much less heat as a result of the lower wattage, so it won’t be effective if you were looking for a cheaper heat lamp.
High-Watt Bulb in Regular-Watt Socket: Problems
We all make mistakes when it comes to home-related things, especially if you are a new homeowner. But some simple mistakes could turn into serious and complicated ones.
Luckily, no experience is needed when reading and adhering to wattage ratings on bulbs and sockets.
But let’s look at the problems that you may face if you fail to adhere to these ratings.
Damage to Wiring
By attaching a high wattage bulb to a regular wattage socket, you run the risk of damage to your socket and the socket wiring.
The extensive heat build-up may overwhelm the socket wiring and cause it to malfunction. This is something you may become forcefully aware of as your wiring starts to smoke!
It may be easier to deal with if it is just a desk lamp, but it can get complicated if the wiring runs through the ceiling or within walls.
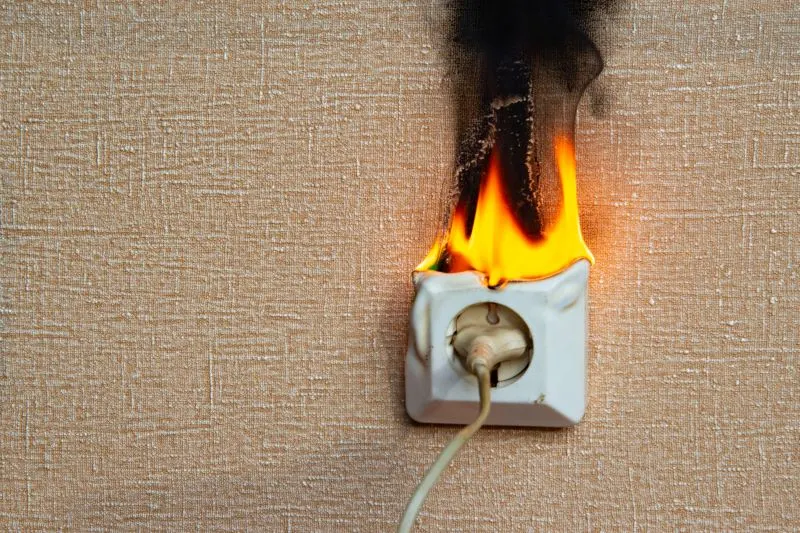
If your house circuit senses that safety is being compromised due to the overwhelming current, the switch trips or the fuse blows and breaks the circuit, relieving the excessive power and preventing the circuit from overheating to the point at which it could easily cause an electrical fire.
Light Fixture Damaged
Most regular lamp sockets are made from plastic. Thus, the high wattage may be too much for the socket to bear, causing it to melt and no longer be functional.
If the circuit is overwhelmed, wiring is damaged, and sockets are melted you also run the risk of an electrical arc occurring as sparks jump from one damaged wire to another.
These electrical arcs are a serious fire hazard and may set fire to lampshades made from wood, bamboo, and other organic and flammable material.

Your curtains that are too closely placed to your burning lampshade may also succumb to the flames, potentially leading to serious destruction of your house.
One also needs to remember that many light fixtures allow for more than one bulb to be fixed, so you need to pay special attention to the total combined wattage, making sure that not all the bulbs are paired with a socket with a lower wattage rating.
Does Red vs White Heat Bulb Matter?
People may believe that different colored bulbs affect the wattage of a bulb. However, this is not true at all. Red and white heat bulbs both produce the same amount of heat.
I think we may just be so used to seeing certain colored lights and associating them with the temperature of the bulb. Some may think that there is a correlation between red heat bulbs and their amplified production of heat.
The only real difference would be the lumens (amount of light emitted) produced by each bulb. For example, in the foodservice industry, they use red heat lamps above their food to keep warm, but the red glow given off by the bulb just gives it the feel and look that the food is warm and fresh.
You would be able to use a white heat bulb in this case and it would keep the food warm just as well as a red heat bulb; it may just not look as warm and desirable.
More pertinently, this means that if you are wanting to use a heat bulb in a regular lamp, opting for a white bulb doesn’t mitigate the chances of overwhelming the circuit.
Sources
https://www.bronsondesign.com/blog/what-is-an-e12-or-e26-light-bulb/
https://uk.rs-online.com/web/generalDisplay.html?id=ideas-and-advice/heat-lamps-guide
https://www.energyrating.gov.au/document/factsheet-light-bulb-buyers-guide
https://www.bulbamerica.com/pages/wattage-voltage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infrared_lamp
https://spyrkaelectric.com/understanding-bulb-wattage-numbers/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lumen_(unit)
https://www.hunker.com/13412823/the-difference-between-regular-heat-lamps-red-heat-lamps
https://www.ehow.com/facts_6300458_color-bulbs-give-off-heat_.html



